Published May 24, 2021 | 4 minute read

Published May 24, 2021 | 4 minute read
When you need to maintain a consistent flow or move high-viscosity materials such as oils, resins and paints, a positive displacement (PD) pump is the ideal choice. With a wide and diverse range of these to choose from, however, picking the right one for your specific application can be confusing.
Here is the Sunair Co. primer on positive displacement pumps.
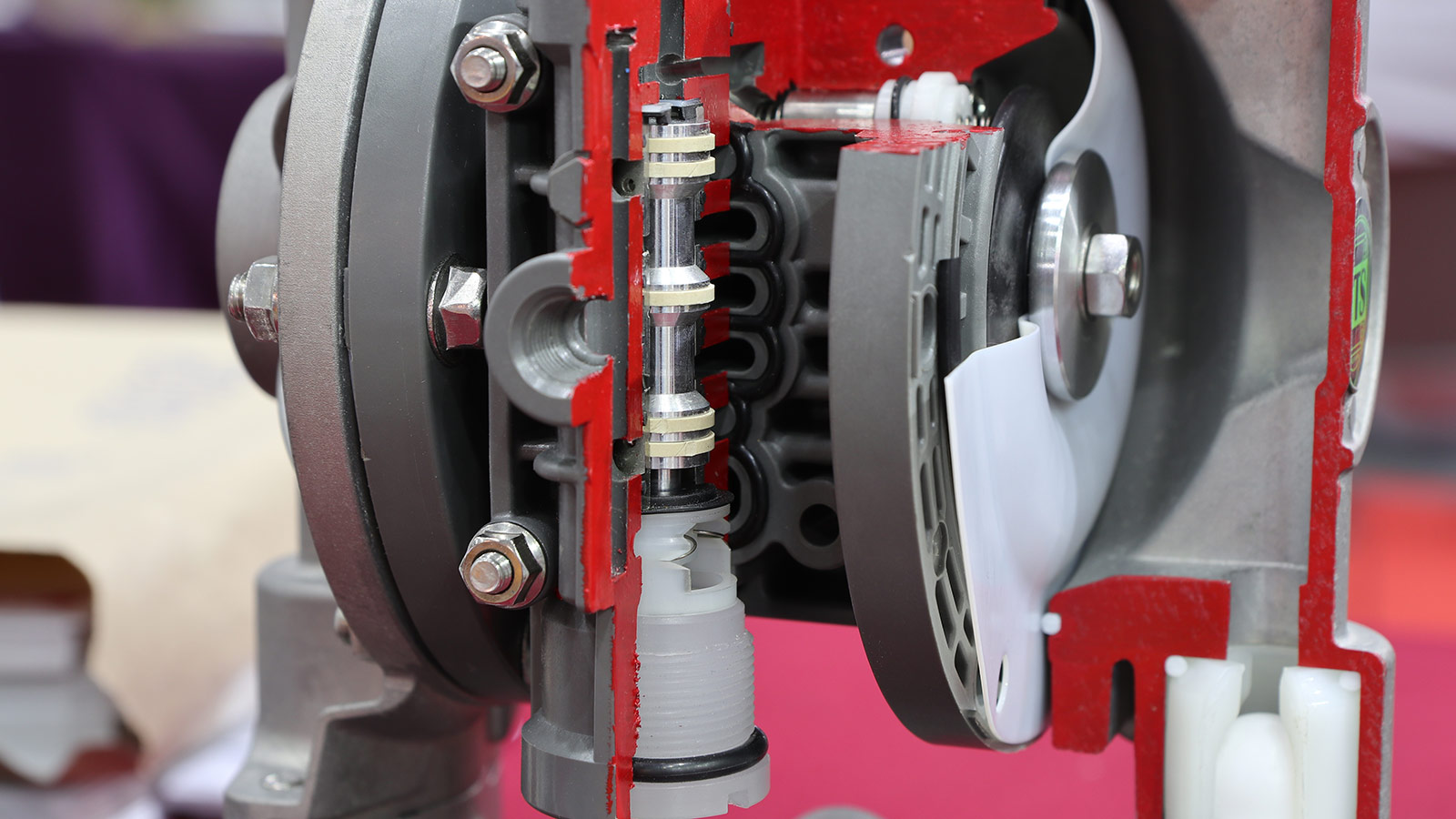
A positive displacement pump transports liquid by utilizing fixed-volume chambers and pistons, plungers, diaphragms, or another driver.
The most important function of a PD pump is its ability to produce the same consistent flow, no matter the discharge pressure. That’s why it’s also called a constant flow machine and employed for a multitude of purposes, across various industries.
There are two main types of PD pumps: rotary and reciprocating. The former features one or more rotor(s), which rotate within a static casing or stator, which create discrete compartments of known volume and deliver relatively smooth flow. A reciprocating pump is analogous to a car engine or your heart. Liquids flow through a valving mechanism into a cylinder or casing and are then stroked back and forth with either one or more pistons, plungers, or diaphragms – or through peristalsis, in the case of a hose pump – releasing it through another valve mechanism in discrete flow pulses into the system.
There are numerous subtypes, including:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Where a centrifugal pump relies on velocity generated by centrifugal force to transport liquid and maintain its flow, positive displacement pumps utilize physical drivers like gears, lobes, vanes, screws, diaphragms, pistons, plungers, or other means to create cavities of fixed volume displacement that expand and contract due to the force of the driver acting on the fluid within the cavities at a rate determined by the speed of the driver.
They feature two cavities and at least one chamber (depending on the type of PD pump): a suction or entry cavity, a transport chamber, and an exit or discharge cavity.
Typical of a rotary PD pump, liquid flows into the suction cavity, which has an expanding volume. The physical driver then holds and advances a fixed volume, regardless of pressure, to the exit cavity. This cavity has a reducing or collapsing volume, which then pushes the liquid out of the pump.
There are many advantages to using a positive displacement pump, but they can all be summed up in one word: adaptability.
PD pumps are useful for myriad purposes, thanks to their ability to handle the following:
|
|
|
|
|
|
The best way to ensure you select the optimal positive displacement pump for your application is to consult with Sunair Co.
Receive the latest industry news, once a month. Unsubscribe anytime.
To determine the size of a component mechanical seal, measure the inside diameter of the seal face, the length of the spring, and diameter and thickness of the stationary seat.
Read NowDesigned to handle various hydrocarbons in accordance with the high standards of the American Petroleum Institute, API pumps ranging from end suction to vertical turbine models are commonly used in the petroleum, petrochemical, and natural gas industries.
Read NowRegularly inspecting your mechanical seals and monitoring various factors that could contribute to failure or leakage will help extend their lifespan, while ensuring operational efficiency and safety.
Read NowPairing Sunair Co.’s high-quality equipment with the most impactful automation opportunities within the food manufacturing industry—across the packaging, production, sanitation, product tracing, and quality control phases—enables companies to realize significant operational efficiencies and cost savings.
Read NowSunair Co. carries high-quality propane pumps and compressors from leading manufacturers such as Sundyne, Blackmer, and National Pump to ensure your operations perform safely and effectively.
Read Now2475 Wyandotte Road
Willow Grove, PA 19090
Phone: (215) 657-9800
Fax: (215) 657-9881
Email: sunairco@sunair.com
© Copyright 2025 Sunair Co.
Logos on this page are copyrights of their respective companies. The Sunair logo is a registered trademark of Sunair Co.
Leave a comment